General Description
DRV8825 is an integrated motor driver chip designed for printers, scanners and other automation equipment. DRV8825 can adjust the current on the motor winding through AVREF/BVREF. The stepping motor must be started within a fixed starting frequency range. After starting, the speed can be increased by increasing the frequency of the drive pulse. The frequency should be increased slowly, and the inertial resistance of the motor will be relatively large when accelerating. The load when the stepper motor is active is divided into two types: inertial load and friction load. The motor is mainly inertial load in the process of accelerating, and it is mainly friction load after the speed is stable.
The chip integrates 2 H-bridge circuits and 1/32 microstepping indexer, which can drive a bipolar motor or two DC brushed motors. The input voltage range is 8.2 ~ 45V, which can provide a drive current of 1.75A, and the chip can provide a peak current of 2.5A at 24V and 25°C. The on-resistance of 0.2 ohm ensures good thermal stability of the chip. At the same time, the chip also integrates short-circuit, overheating, under-voltage, and cross-conduction protection circuits, which can detect fault conditions and quickly cut off the H-bridge, thereby providing protection for the motor and drive chip.
The driver module is usually used in automated teller machines, money processing machines, video surveillance cameras, printers, scanners, office automation machines, game consoles, factory automation, and robotics.
How to use the DRV8825 driver module
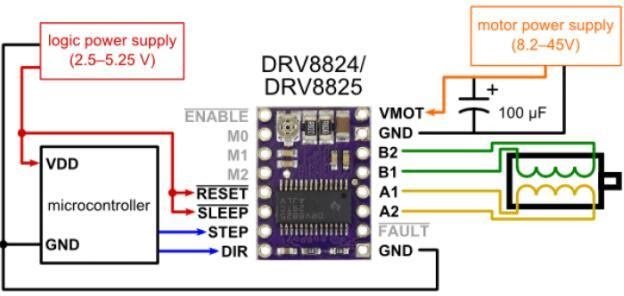
The interface diagram of DRV8825 is shown below. With DRV8825, you can use a few pins to control a stepper motor. The pins and interfaces of this module are almost the same as those of the A4988 stepper motor driver bracket.
As shown in the figure above, the DIR, STEP and FAULT pins of the module are connected to the microcontroller to drive the stepper motor. The STEP pin is used to control the step, and the DIR pin is used to control the direction. DRV8825 also has a FAULT pin, which is short-circuited with the SLEEP pin. Therefore, whenever the FAULT pin driven is LOW, the entire chip is disabled. The microstep pins (M0, M1 and M2) are used to operate the driver module with different step functions. In the above circuit, the M0, M1 and M2 pins remain disconnected, which means that the driver will work in full-step mode. The DRV8825 has a low ESR ceramic capacitor onboard, making it susceptible to voltage spikes. Therefore, it is recommended to place at least a 47μf capacitor between the power supply pins of the motor. It is usually used to control NEMA series stepper motors such as NEMA17, NEMA23, and NEMA34.
DRV8825 driver module pin diagram
DRV8824/8825 even includes the common A4988 motor drive module. The pin connection mode is not much different. In the above figure, M0, M1, and M2 are not connected, it is high level, and the working mode of the drive board is 32 subdivisions. If you need to set it for other subdivision modes, refer to the following table for circuit modification, that is, M0, M1, and M2 are grounded separately or all to achieve different operating modes. Subdivision setting table of DRV8825 drive module:
DRV8825 IC 2D model
Layout precautions of DRV stepper motor driver
Pay attention to the heat dissipation treatment when laying out the DRV. The power supply (LDO, DC-DC) should be as far away as possible from the DRV. The surrounding wiring should not be too close to the DRV and there must be a certain amount of space. The wiring will affect the heat dissipation. The 0th pin of the DRV is a heat sink. It is best to weld the bead to the board and punch through holes to the back of the board to dissipate heat. sprunki horror Endless Fun Awaits!