How to boost your immune system (vitamin c): The human body works efficiently through the coordinated function of several systems, including the nervous system, immune system, digestive system, circulatory system, excretory system, and reproductive system.
Among them, the digestive system and the immune system play a crucial role in growth and development.
A healthy and robust immune system aids in building an efficient digestive system. Alternatively, a perfectly functioning digestive system nourishes the body and maintains healthy immune cells to fight against diseases and microbes.
Let us have an idea of the digestive and immune systems, and the effective ways of boosting these systems.
What is the function of the digestive system?
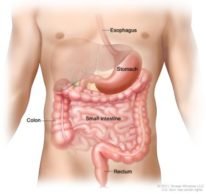
The digestive system helps in breaking down food into the simplest molecules and their absorption by the cells and tissues. It consists of the alimentary canal-a continuous tube initiating with the mouth and ending at the anus.
The entire process takes place through several phases, including ingestion, propulsion, secretion of digestive enzymes, breaking down of food, and absorption.
Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, pancreas, small intestine, and large intestine are all crucial organs of the digestive system.
There are two forms of digestion- mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. In the former, the food gets broken down into smaller parts through chewing and muscular churning of the stomach.
In chemical digestion, food gets chemically broken down into simple molecules.
What is the function of the immune system?
The immune system consists of warriors of our bodies. They are vital for fighting against microbes and diseases. White blood cells, lymphatic system, antibodies, thymus, spleen, and bone marrow are crucial members of the immune system. They also keep a record of all germs that invade our body through B- and T-lymphocytes, so that they can at once recognize and defeat them on re-entry. Immune cells do not allow pathogens to multiply in our system and cause diseases. However, if we do not take care of the immune system, then immune cells would become weak and result in largescale infections.
Methods of Boosting the Immune System for a Healthy Digestive System
Now that we have got a comprehensive idea of the functions of the digestive and the immune system to let us go ahead with some tried and tested ways of boosting these crucial organ systems of the human body.
Consuming Fresh and Nutritious Food || How to boost your immune system (vitamin c)
Include a generous amount of fresh fruits, vegetables, herbs, spices, dairy products, and seafood in your diet. Studies reveal that spices like clove, oregano, cumin, and thyme have excellent antimicrobial properties.
They can decrease the incidence of bacterial infection, like Bacillus subtilis pseudomonas aeruginosa Citrus fruits like oranges, grapes, and tangerines, red pepper, and cruciferous vegetables also offer an abundant supply of vitamin C to our body, which is essential for fortifying the immune system. Half a cup of red pepper can provide 95 milligrams or 106 percent of the daily dose of vitamin C or supplement according to physician advice.
A study published in 2017 in Nutrients revealed that vitamin C helps in improving both the innate and adaptive immunity of human beings.
Proteinaceous diet from eggs, fishes, lean meat, poultry, and lentils also helps in nourishing the immune cells. Another study published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases in 2013 pointed out that rats consuming a ‘low-protein diet’ (only 2 percent protein) became more susceptible to the flu virus than those having a ‘normal-protein diet’ (18 percent protein). Fresh fruits and vegetables also have a positive impact on the gut. People suffer from fewer diseases in the digestive tract when they have nutritious meals. How to boost your immune system (vitamin c)
Sleeping Adequately
Researches have established that the human body produces and distributes immune cells when individuals get sufficient good quality sleep. At least seven hours of sleep is essential for the optimum functioning of the immune system. Sleep-deprived people do not have an adequate level of Cytokines (a protein fighting inflammation), interleukin 12, and T cells. Their immune system is unable to defend the body against severe diseases and infections. A study Behavioral Sleep Medicine in 2017 reported that healthy young adults who have insomnia have a high risk of being infected by the influenza virus. Even if they receive a vaccination, against the infection, their immune system is unable to ward off the virus. Inadequate sleep also elevates cortisol levels, which suppresses the immune system.
Managing Stress
According to Modern Medicine, a symbiotic relationship exists between the mind and body. When the mind is not in good spirits, it can have a toll on the health as well. Chronic stress harms both the immune as well as the digestive system. It limits the oxygen flow in the blood and causes stomach cramps and imbalance in gut bacteria. Gastrointestinal (GI) disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and peptic ulcers increase in patients suffering from long-term stress and depression.
Stress and anxiety also cause an increased secretion of cortisol, which can result in inflammation and an overactive digestive system. Many patients complain of allergies and autoimmune disorders as a result of long-term stress. Doctors advocate sufferers to lean towards a healthy lifestyle and meditate for at least 10 minutes a day to keep stress at bay. It will help you rewire the brain and usher a confident approach to life.
Regular Exercises
Regular exercises are beneficial in warding off a host of diseases. Thirty minutes workout daily can significantly reduce the risk of various chronic illnesses like diabetes, cardiac ailments, and obesity. According to a 2019 scientific review published in the Journal of Sport and Health Science, exercises boost the metabolic health and also have an anti-inflammatory influence on the human body mediated through multiple pathways.
See Also: Are-protein-bars-really-healthy
Immune cells in the body like to aggregate near the lymphoid organs like the spleen and liver. Regular exercises help in circulating these fighters throughout the system and kill pathogens. Workouts also promote the synthesis of specialized immune cells (T cells), which can find microbes like bacteria and viruses and negate them. Exercises like brisk walking, cycling, and crunches stimulate the digestive system and prevent bloating.
Quitting Smoking
Cigarette smoke contains a range of hazardous compounds, including nicotine, carbon monoxide, cadmium, and nitrogen oxides. According to a review published in the Oncotarget in 2016, these harmful molecules adversely affect the production and circulation of immune cells (cytokines, T cells, and B cells). Smoking also retards the prognosis of several infections, including influenza, pneumonia, tuberculosis, GERD, peptic ulcers, and Crohn’s disease. Studies suggest that passive smoking is as harmful as direct smoking.
How to boost your immune system (vitamin c): Smokers can take the help of nicotine replacement therapy (use of nicotine gums, nasal spray, patches, inhalers, and lozenges) to ditch the cigarette forever.
These were some of the tried and tested ways of boosting the immune system and nurturing a healthy digestive system. sprunki horror Endless Fun Awaits!